|
This document is referring to a past Scout release. Please click here for the recent version. Looking for something else? Visit https://eclipsescout.github.io for all Scout related documentation. |
About This Release
Eclipse Scout 7.0 is part of the Eclipse Oxygen release. It was released in June 2017 (release schedule), with the Service Release 3 released in March 2018. The latest version of this release is 7.0.300.005_Oxygen_3.
|
If you are upgrading from version 6.0, please also read the release notes for the 6.1 (Oxygen preview) release: https://eclipsescout.github.io/6.1/release-notes.html |
You can see the detailed change log on GitHub.
Service Releases
The following changes were made after the initial 7.0 release (Eclipse Oxygen release). The following notes relate to a service release.
Oxygen.1 (7.0.100) Released on September 27, 2017
Detailed change log: https://github.com/eclipse/scout.rt/compare/7.0.0.008_Oxygen…7.0.100.017_Oxygen_1
Obtaining the Latest Version
Runtime (Scout RT)
Scout RT artifacts are distributed via Maven:
-
7.0.300.005_Oxygen_3 on Maven Central
-
7.0.300.005_Oxygen_3 on mvnrepository.com
Usage example in the parent POM of your Scout application:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.eclipse.scout.rt</groupId>
<artifactId>org.eclipse.scout.rt</artifactId>
<version>7.0.300.005_Oxygen_3</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>Eclipse IDE Tooling (Scout SDK)
You can download the complete Eclipse IDE with Scout SDK included (EPP) here:
Eclipse for Scout Developers
To install the Scout SDK into your existing Eclipse IDE, use this update site:
http://download.eclipse.org/scout/releases/7.0/7.0.300/005_Oxygen_3/
Demo Applications
The demo applications for this version can be found on the features/version/7.0.300.005_Oxygen_3 branch of our docs repository on GitHub.
If you just want to play around with them without looking at the source code, you can always use the deployed versions:
Upgrade to jQuery 3
We upgraded from jQuery 2.1.4 to jQuery 3.2.1. The new version contains a lot of improvements, including performance optimizations for animations and event handling. It also allowed us to remove some code which is now included in jQuery directly (e.g. addClassSVG, removeClassSVG, hasClassSVG).
Beside upgrading jQuery, we upgraded the Jasmine Maven Plugin to version 2.2 and the PhantomJS Maven Plugin to version 2.1.1, too. The YUI compressor has also been upgraded from 2.4.8 to version 2.4.9, but unfortunately it is not compatible with jQuery 3. To make it work again we had to fork it and now use the version 2.4.9-BSI-1.
Along with the jQuery upgrade we decided to remove jQuery UI and jQuery Mobile completely. Scout only included parts of these libraries and the usage was limited to 2 or 3 functions. Without these dependencies it will be easier in the future to upgrade jQuery itself.
Scout JS
With release 6.1 first steps had been taken to allow creating Scout applications with JavaScript only (see 6.1 Release Notes). The development has been continued so that the current release comes with a cleaner API, more working widgets and even some documentation (Tech Doc) and sample code (https://scout.bsi-software.com/jswidgets/). Still, it has not been finished yet and will be improved with the upcoming service releases. Let us know what you think!
It is important to note that Scout JS is not a separate framework. It actually just names the JavaScript part of the Scout framework. Classic Scout applications use it as well. This means effort made in this area also improves the stability of the Scout framework itself and even makes the development of custom widgets easier.
Validators, Parser and Formatter (JS)
The ValueField.js now provides an API to add custom parse, validate and format logic. This is especially useful for the StringField, but you may also use it for the NumberField and the DateField. See the technical guide for details.
Simplified API (JS)
The parameter $parent is now optional when calling widget.render(). The $parent may be resolved using this.parent. No need to always write
widget.render(this.$container) anymore, instead just write widget.render() if the $container of the parent should be used as $parent.
The property change event has been simplified. Instead of newProperties, oldProperties and changedProperties, the event now contains propertyName, oldValue and newValue. This makes handling the event easier.
DateField, StringField and NumberField now use the value based API provided by ValueField. This means you can write the value using field.setValue(value), and read it using field.value. The validators and formatter will be called accordingly.
Logical Grid Validation (JS)
When writing a Scout Form with Java, you don’t have to care about the logical grid. You only have to specify some grid hints like width and height of a cell. The positioning of the cell is calculated automatically by the logical grid.
This is now also possible with JS based Scout applications. There is no need to manually create a Logical Grid (e.g. VerticalSmartGroupBoxBodyGrid or HorizontalGroupBoxBodyGrid and validate it anymore, this will be done automatically by the LogicalGridLayout itself.
New HTTP Abstraction Layer: Google HTTP Client for Java
The org.eclipse.scout.rt.shared.servicetunnel.http.HttpServiceTunnel class and other HTTP usages were changed to use the Google HTTP Client Library for Java 1.22. This library adds a HTTP abstraction layer and allows to use different low-level libraries like java.net.HttpURLConnection (one and only layer used in previous versions) or Apache HTTP Client 4.5.3 (new default).
Different HTTP clients with different parameters (even with different low-level libraries) may be used and kept using (custom) implementations of org.eclipse.scout.rt.shared.http.IHttpTransportManager. Currently there are two internal implementations of this interface: HttpServiceTunnelTransportManager (only used by the service tunnel) and DefaultHttpTransportManager (used for all other HTTP connections).
The following new configuration properties (none of them is required to be set, defaults are provided for all of them) were added:
-
scout.http.transport_factory, possible values areorg.eclipse.scout.rt.shared.http.ApacheHttpTransportFactory(default, see above),org.eclipse.scout.rt.shared.http.NetHttpTransportFactory(to use previous HttpURLConnection layer) or any custom implementation of anorg.eclipse.scout.rt.shared.http.IHttpTransportFactory.
For the HttpServiceTunnelTransportManager:
-
org.eclipse.scout.rt.servicetunnel.apache_max_connections_per_route, maximum number of connections per route (default: 2048, only applicable for for Apache HTTP Client). -
org.eclipse.scout.rt.servicetunnel.apache_max_connections_total, maximum number of connections in total (default: 2048, only applicable for for Apache HTTP Client).
For the all other org.eclipse.scout.rt.shared.http.AbstractHttpTransportManager (if not overriding these settings):
-
scout.http.apache_connection_time_to_live, time to live (milliseconds) for kept alive connections (default: 1 hour, only applicable for Apache HTTP Client). -
scout.http.apache_max_connections_per_route, maximum number of connections per route (default: 32, only applicable for Apache HTTP Client). -
scout.http.apache_max_connections_total, maximum number of connections in total (default: 128, only applicable for Apache HTTP Client).
For each Apache HTTP Client created using the org.eclipse.scout.rt.shared.http.ApacheHttpTransportFactory (by default each org.eclipse.scout.rt.shared.http.IHttpTransportManager using the Apache HTTP Client) their own org.eclipse.scout.rt.shared.http.ApacheMultiSessionCookieStore and org.eclipse.scout.rt.shared.http.proxy.ConfigurableProxySelector (see javadoc for detailed description and configurability) are created. These instances are therefore not registered globally for the java virtual machine anymore.
Support for REST Services
The following new Scout modules have been added to support REST services with Jackson as marshaller:
-
org.eclipse.scout.rt.rest -
org.eclipse.scout.rt.rest.test -
org.eclipse.scout.rt.jackson -
org.eclipse.scout.rt.jackson.test
The most important class is the org.eclipse.scout.rt.rest.RestApplication which searches for all implementations of IRestResource and exposes them as REST services. It also registers ExceptionMappers and setups Jackson to work with Jandex.
So if you want to use REST services, you could use the Jersey REST servlet (org.glassfish.jersey.servlet.ServletContainer), pass the RestApplication as parameter and install the org.eclipse.scout.rt.server.context.ServerRunContextFilter to have the proper run context for every REST call. Creating the REST resource is straight forward using the annotations from javax.ws.rs. Just make sure the resource implements the interface IRestResource so that it will be registered by the RestApplication on startup.
Prevent Double Clicks on Buttons and Menus
If a button or a menu is clicked twice within a short period of time, the corresponding action is executed twice. This can be convenient (e.g. when inserting new rows in a table) or unproblematic (e.g. when closing a form - the second click will just be ignored). However, there are cases where executing an action twice would break things. To instruct the UI to block double clicks, a new property "preventDoubleClick" is provided on buttons and menus:
-
AbstractButton.getConfiguredPreventDoubleClick() -
AbstractMenu.getConfiguredPreventDoubleClick()
The default value is false.
Minimized Mode for Split Box (since 7.0.100)
The SplitBox widget now supports a minimum splitter position according to the collapsible field. The collapsible field size is limited between minimum splitter position and maximum available size. The collapse buttons now toggles between three modes of the collapsible field: default, minimized and collapsed. The default value for minimal splitter size is null, which means, no minimal splitter size is set and no change in existing behavior.
New API methods on AbstractSplitBox:
-
Double getMinSplitterPosition() -
void setMinSplitterPosition(Double minPosition) -
Double getConfiguredMinSplitterPosition() -
boolean isFieldMinimized() -
void setFieldMinimized(boolean minimized) -
boolean getConfiguredFieldMinimized()
Additional to the existing three splitbox position types a new SPLITTER_POSITION_TYPE_RELATIVE_SECOND type was added. This new splitter position type allows to specify the size of the second field relative to the full size of the splitbox.
Split Box Keystrokes
The former AbstractSplitBox.setCollapseKeyStroke() and AbstractSplitBox.getCollapseKeyStroke() methods were deprecated and renamed, since the configured keystroke toggles between collapsed and default size of the collapsible field.
Renamed methods:
-
AbstractSplitBox.setToggleCollapseKeyStroke(String keyStroke) -
AbstractSplitBox.getToggleCollapseKeyStroke()
New API methods to define keystrokes allowing to toggle between default, minimized and collapsed mode. The First keystroke corresponds to the left button for a vertical split boxe and the top button for a horizontal splitbox. The Second keystroke corresponds to the right button for a vertical split boxe and the bottom button for a horizontal splitbox.
New API methods:
-
AbstractSplitBox.setFirstCollapseKeyStroke(String keyStroke) -
AbstractSplitBox.getFirstCollapseKeyStroke() -
AbstractSplitBox.setSecondCollapseKeyStroke(String keyStroke) -
AbstractSplitBox.getSecondCollapseKeyStroke() -
AbstractSplitBox.getConfiguredToogleCollapseKeyStroke() -
AbstractSplitBox.getConfiguredFirstCollapseKeyStroke()
New Smart Field: ISmartField2 (since 7.0.100)
This release introduces a new smart field: ISmartField2. It has almost the same interface as the old smart field ISmartField, which still exists
in this Scout release, but will be removed with 7.1. The main differences to the old smart field:
-
In "Scout classic" (with a Java UI server) there is no longer a model representation of the proposal chooser. In the new smart field the whole state of the proposal chooser is kept on client side in the browser. The Java UI server only sends lookup rows to the client. Depending on the smart field configuration
SmartField2.jswill render either a proposal chooser with a table or a tree (hierarchical). It’s still possible to replace the default proposal chooser, but now you have to write a bit of JavaScript code to do that. -
The smart field can now be used with Scout JS. This means you’re no longer restricted to "Scout classic" when you want to use a smart field and you can use the smart field with any static or dynamic data source, for instance a REST service. Take a look at the jswidgets demo app to see examples how to use the smart field with JavaScript.
Migrating from ISmartField to ISmartField2 should be simple in most cases, since the interfaces of the old and the new smart field are almost identical. Differences are:
-
There is no longer a
IMixedSmartFieldwith two generic types for VALUE and LOOKUP_TYPE, since these two types are identical in 99.9% of all cases. When you migrate an old Scout application that uses different types you could either provide a new LookupCall that has the same lookup type as the smart field value, or you could simply cast the value of the smart field where needed. -
The value of the proposal field is now always a String. The generic type you pass to the proposal field is the lookup type. Use the methods
setValueAsStringandgetValueAsStringto read and write the value of the proposal field. Additionally you can still access the selected lookup row of the proposal field and get the key of the lookup row. When you have an existing LookupCall which has a type other than String (for instance a Java bean), you should use Object as generic type for the proposal field and cast where required. This may be the case when you have overridden thevalidateValue()method, for instance. If you don’t do that, you may notice ClassCastExceptions, because as mentioned above, the value of the proposal field is now always a String. Also note that the value of the proposal field is not the selected lookup row or the key of the selected lookup row. The value is simply the text of the selected lookup row. If you need a property of the selected lookup row, usually thekeyproperty, you must check if there is a lookup row selected by callinggetLookupRow()and access the property from that object. Also note that the proposal field does never select a lookup row when you set a value. -
When you migrate an old Scout application that has a custom proposal chooser, you should probably create a custom JavaScript implementation for your smart field. There you can override the behavior of the default implementation.
Note: With 7.1 the old smart field will be deleted and replaced by the new smart field ISmartField2, additionally in 7.1 ISmartField2 will be renamed to ISmartField again. When you start a new Scout project with this release you should use ISmartField2.
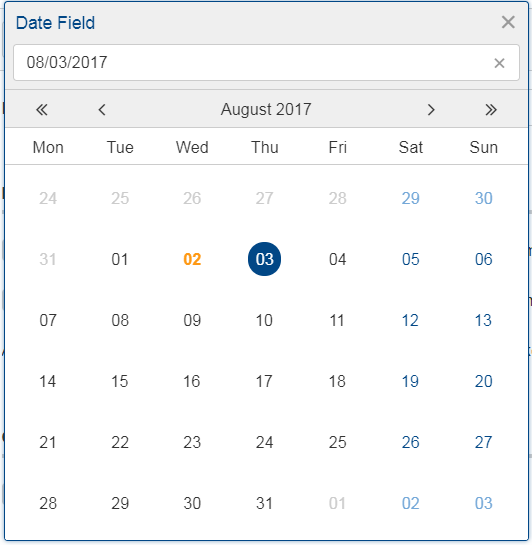
Time Picker for Date Field (since 7.0.100)
The date picker has been there for a long time and provides a convenient way to pick a date. To enter a time however, you had to use the keyboard. These days are now gone because with this service release a time picker has been added. It shows the hours from 0 to 23 and the commonly used minutes. The resolution is configurable, so you could change to 00, 15, 30, 45 instead of 00, 30 if you want. You can still use your keyboard, though.

Clear Icon for Input Fields (since 7.0.100)
Every input field now has a clear icon. It is active while the field has the focus. This makes it easy to clear the input with one click.
Improved Touch Popups (since 7.0.100)
When using the smart field or date field on a mobile phone or tablet, the popup will be shown in a different way to make it easier to pick a value with the finger. This existing behavior has been improved so that it is now easier and more intuitive to clear the value and close the popup.
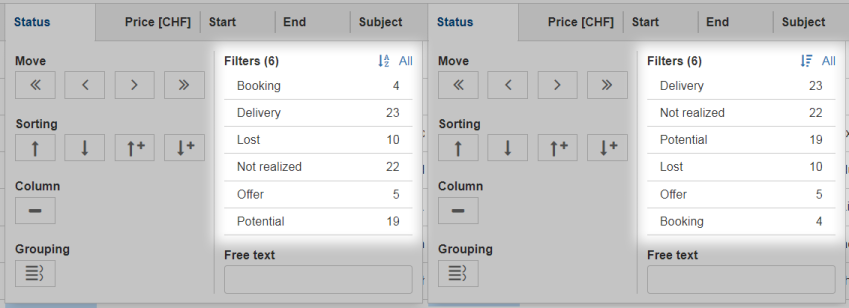
Sorting of Filter Table (since 7.0.100)
The column header menu shows a list of all the different values which occur in the cells of that column. If one of these values is selected the table will be filtered and will only show rows which contain that value. These values are sorted alphabetically. Because sometimes it might be useful to only display the rows which contain the most used values, a possibility was added to sort the values by the number of occurrences. Just press the icon on the left of the 'All' button.
Auto Optimize Column Width (since 7.0.100)
The column has a property called autoOptimizeWidth. This property has been there for a while but has not been interpreted yet. With 7.0.100 the support for this property has been implemented. If you set it to true on a specific column, the column will always be as width as its content. If not set, the user can still optimize the width manually by double clicking the separator between two columns.
New Property Auto Optimize Column Max Width (since 7.0.300)
The new property autoOptimizeMaxWidth determines the maximum width a column will grow to when it is auto optimized when autoOptimizeWidth is set to true. The user may still manually make columns wider by dragging or double-clicking the column separators.
New Property for Request Timeout (since 7.0.100)
Every UI request schedules a model job to process the user interaction and waits for this job and other scheduled model jobs to complete. During that time the ui is blocked but the user may abort the processing manually by clicking cancel. If the user does not cancel it and it takes too long to complete the model jobs are now aborted automatically to free resources. The default is set to 1 hour but you may configure it by using the new property scout.ui.model.jobs.await.timeout (the unit is seconds). After the abortion a message box is displayed to the user saying the request timed out.
Minor Changes for HTTP Abstraction Properties (since 7.0.100)
-
Existing configuration property classes have been bundled in two
org.eclipse.scout.rt.shared.http.HttpConfigurationPropertiesandorg.eclipse.scout.rt.shared.servicetunnel.http.HttpServiceTunnelConfigurationPropertiesclasses. -
The configuration property
org.eclipse.scout.rt.servicetunnel.apache_connection_time_to_livehas been removed (scout.http.apache_connection_time_to_liveis used instead). -
New configuration properties have been added:
-
scout.http.apache_keep_alive(possible values: true/false), whether to use keep-alive connections. If property is not set the system propertyhttp.keepAliveis evaluated, if this system property is also not set true will be used as a last resort. -
scout.http.apache_retry_post(possible values: true/false), whether to retry HTTP POST requests. If not property is not set the system propertysun.net.http.retryPostis evaluated, if this system property is also not set true will be used as a last resort.
-
Desktop Splitter Position Remembered Across Sessions (since 7.0.300)
The position of the desktop splitter position (between the navigation and the bench) is now persisted across sessions, i.e. the previous setting will be restored even after you closed your browser. The position is stored in the HTML 5 local storage provided by the local browser. It is therefore a device-specific setting, which is especially useful when accessing the same application through screens with different resolutions.
In case the splitter position should never be remembered, the feature can be disabled globally by setting the property cacheSplitterPosition on the desktop to false.
No Value in JS for String Fields With Masked Input (since 7.0.300)
A string field with masked input did send the value from the model to the UI layer allowing to read possibly sensitive data via JS. The value is not sent to the UI layer anymore resulting in a slightly different behavior. From the model perspective nothing changed.
-
A
valueproperty change in the model will send an obfuscated display text instead of the real display text to prevent data leakage. -
On focus of the input field, the obfuscated text is removed, showing an empty input field. On blur, if nothing was typed, the obfuscated text is restored (model value is unchanged).
-
When text is typed into the input field, the display text represents the real display text (but is still masked).
Menus in the Status Tooltip of a Form Field (since 7.0.300)
A form field can have menus which can be displayed by clicking the ellipsis icon on the right side of the field. A form field can also have a tooltip which can be displayed by clicking the info icon on the right side of the field. In fact, the ellipsis icon and the status icon are at the same position and called status icon. It is called like this because it even has a third purpose: to display the error status. Because this icon has multiple purposes it has to be defined what happens when the icon is clicked. Until now, if an error status was shown, the menus were not available.
Until Scout 6.1. the problem was the same for tooltips. One had to decide which was more important: tooltip or menus. With Scout 6.1 a combination has been introduced: the tooltip now also shows the menus. But the problem still existed for error status. The reason is: not every menu makes sense when displayed along with the error status message. But there are menus which make sense and should be displayed. And this case is now supported.
It is now possible to define which menus should be displayed in an error status. It is also possible to bind the menu to certain status codes or severities. Let’s say you want to display the menu if a smart field does not find any results, then you can bind the menu to the ISmartField.NO_RESULTS_ERROR_CODE. Or you can bind it to custom error codes for your custom status messages. See the Java Doc of IStatusMenuMapping for details.
| Do you want to improve this document? Have a look at the sources on GitHub. |